Within the Intertropical Zone are the Jungle Ecosystems. The diversity of these ecosystems forced the differentiation by types such as the Cloud Forest, Gallery Forest, Rainforest and others. In the basin of the Caribbean Sea the forests with the easiest access are in Central America, other patches of rainforest and tropical forests are found among the mountains of the Antilles Islands as there are in the Dominican Republic. In Venezuela, in the chain of mountains facing the sea is the Cloud Forest, as in other places at the foot of the Andean mountain. To the north of the Caribbean Sea this ecosystem exist only in the Yucatan peninsula.
The cloud forest biome is directly related to the atmospheric cloudiness of mountainous areas because they favor the formation of clouds during most of the year. The altitudinal range of the cloudiness is between 2953 and 6562 feets above sea level and it is where the Cloudy Forests develop.
The cloudiness together with the altitude is the most important environmental variable in the Cloud Forest, directly influencing the temperature and precipitation that define its ecology. The Cloud forest Biome is as complex as the Coral Reef, and notable for its biodiversity as well as a high rate of endemism.
Otto Huber (1986), differentiates three types of cloud forest related to altitude:
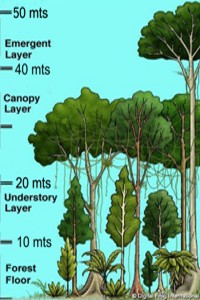
Transitional Rainforest, is between 2953 and 4101 feets over sea level, rainfall is 65 inch / year and temperature of 69.8°F and is characterized by having species from the neighboring semi-deciduous ecosystem along with the own jungle. Three strata can be differentiated: Upper layer between 98 and 164 feets with large tree species such as Gyranthea caribensis (photo). Medium stratum between 33 and 98 feets formed by a mixture of species from both ecosystems. Low stratum, with trees less than 33 feets high, of which many are juvenile trees and palms (Bactris setulosa, Euterpe sp, Geoma pinnatifrons). The presence of climbing plants is typical of the low stratum together with the epiphytes that are also found in the other strata.
 |
 |

Typical Rain Forest, is between 4101 and 5249 feets above sea level, the rainfall is 63 inch/year and the average temperature is 66.2°F. Two altitudinal strata are presented: Upper stratum with its main characteristic of being formed by an exuberant and biodiverse flora and fauna. The height of the canopy is between 164 feets, the characteristic species are Eclinusa sp. Chimarris microcarpa and many palms. The trees are also the support of a rich community of epiphytes, bromeliads and orchids.
Higher Cloud Forest, is between 5249 and 6562 feets over sea level, the rainfall is 79 inch/year and the average temperature 59°F. The arboreal vegetation is of medium height between 26 and 66 feets forming a single stratum, are very characteristic for their abundance the palms like Euterpe sp., Ceroxylon vogelianum, Geonoma undata.
Wildlife
The fauna of the Cloud Forest along with the flora is remarkable for its biodiversity, mentioning some is unfair with respect to all others. This jungle is mainly represented by insects
Birds
Presence of mammals is small. Among the most visible and possible to find for being the largest are the jaguar (Panthera onca) along with other species of smaller size, the Hoffmann's two-toed sloth (Choloepus hoffmanni) in the tree canopy with the herds of monkeys araguatos (Alouatta seniculus) and many more.
|