|
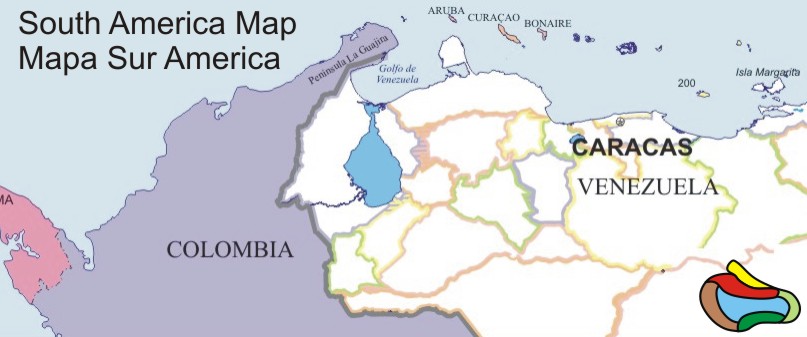
The coast that South America has with the Caribbean Sea is of a length of approximately 3106.9 miles belonging to Venezuela and Colombia. In front of these coasts there are important islands like the Netherlands Antilles (Islands of Aruba, Curacao and Bonaire), Trinidad and Isla Margarita in the eastern end, as well as multiple islands and coral atolls off the coast of Venezuela.
The coasts of South America not only offer places of tourist interest like many other places of the Caribbean Sea, but also others such as the Cloud Forest and mythical places like the Tabular Mountains of the Tepuyes or steep mountains such as the Andes with their peaks that rise up to the 16404.2 feetss and multiple forts and fortresses on the coast with special relevance to Cartagena de Indias (Colombia) and many others on the coast of Venezuela.
The Caribbean climate of the coast of South America does not differ greatly from that of the rest of the Caribbean Sea basin, with two seasons well marked by the preccionacion and average annual temperatures over the 77°F.
The geology is completely different from de caribbean because the coast belongs to the Plate of South America. On it predominate the geological faults that are in constant general movement and some times earthquakes of intensities around the 7.5 of the scale. Inland are the foothills of the Andes mountain range between Venezuela and Colombia and the Coastal Mountain range in Venezuela.
The history of the South American Carbbean goes back to the pre-Columbian era with the Arawack and the Caribbean tribes, none of these cultures ever had the development of the Mayans of Central America. The Spanish constructions during the long colony are multiple, in Colombia the city of Cartagena de Indias is the largest center with important colonial constructions that together with those of Cuba among all of those existing in the Caribbean Sea are the most relevant. In the Venezuelan territory the constructions are many although smaller.
The naturae, once again, as in the entire Caribbean Sea Basin is very diverse both at sea and on land with its characteristic endemism that differentiates it from other sectors.
The Island of Margarita is the largest of a set of three, which form the Nueva Esparta State of Venezuela. They are located in front of the mainland of South America, in waters of the Caribbean Sea, at 11º North and 64º West. The islands of Curacao, Aruba and Bonaire are also very much visited by the tourists as well as the Islands of San Andres that belongs to Colombia.
 |
 |
Venezuela |
 |
| |
|
Estado Anzoátegui |
| |
|
|
Islas Chimanas |
|
| |
|
|
Islas Borrachas |
|
| |
|
|
Isletas de Píritu |
|
| |
|
Estado Carabobo |
| |
|
|
Isla Larga |
|
 |
 |
Estado Nueva Esparta |
| |
|
|
Isla de Margarita |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Coche |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Cubagua |
|
| |
|
Estado Sucre |
| |
|
|
Islas Caracas |
|
| |
|
Dependencias Federales Venezolanas |
| |
|
|
Archipiélago Los Monjes |
|
| |
|
|
Archipiélago Las Aves |
|
| |
|
|
Archipiélago los Testigos |
|
| |
|
|
Archipiélago Los Frailes |
|
| |
|
|
Isla Los Hermanos |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Aves |
|
| |
|
|
Isla la Sola |
|
| |
|
|
Isla la Tortuga: Cayo Herradura, Islas Los Tortuguillos |
|
| |
|
|
Isla la Orchila |
|
| |
|
|
Isla la Blanquilla |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Patos |
|
 |
 |
|
Archipiélago Los Roques: Gran Roque, Francisquí, Isla Larga, Nordisquí, Madrisquí, Crasquí, Cayo Espenquí, Cayo Carenero, Cayo de Agua, Dos Mosquises, Cayo Sal, Cayo Grande |
|
| |
|
Estado Zulia |
| |
|
|
Isla de San Carlos |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Toas |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Zapara |
|
| |
|
|
Isla Los Pájaros |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Pescadores |
|
| |
|
|
Isla de Providencia |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Colombia |
 |
|
|
Departamento de San Andrés, Providencia y Santa Catalina |
|
|
|
Isla de San Andrés |
|
|
|
|
Isla de Providencia |
|
| |
|
|
Isla Santa Catalina |
|
| |
|
|
Albuquerque |
|
| |
|
|
Bajo Nuevo |
|
| |
|
|
Cayo Bolívar |
|
| |
|
|
Cayo Roncador |
|
| |
|
|
Cayo Rocoso |
|
| |
|
|
Cayo Santander |
|
| |
|
|
Cayo Serranilla |
|
| |
|
|
Serrana |
|
| |
|
|
Quitasueño |
|
| |
|
Departamento de Bolívar |
| |
|
|
Isla Tierra Bomba |
|
| |
|
|
Islas del Rosario |
|
| |
|
Departamento de Sucre |
| |
|
|
Archipiélago de San Bernardo |
|
|
 |
 |
Países Bajos |
 |
| |
|
Antillas Holandesas |
| |
|
|
Bonaire: Pequeña Bonaire |
|
| |
|
|
Curazao: Pequeña Curazao |
|
| |
|
|
Saba |
|
| |
|
|
San Eustaquio |
|
| |
|
|
San Martín |
|
 |
 |
|
Aruba |
 |
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Trinidad y Tobago |
 |
|
| |